how are work and energy related explain the work-energy theorem
Start date Apr 6 2015. Translational kinetic energy is distinct from rotational kinetic energy which is considered later In equation form the.
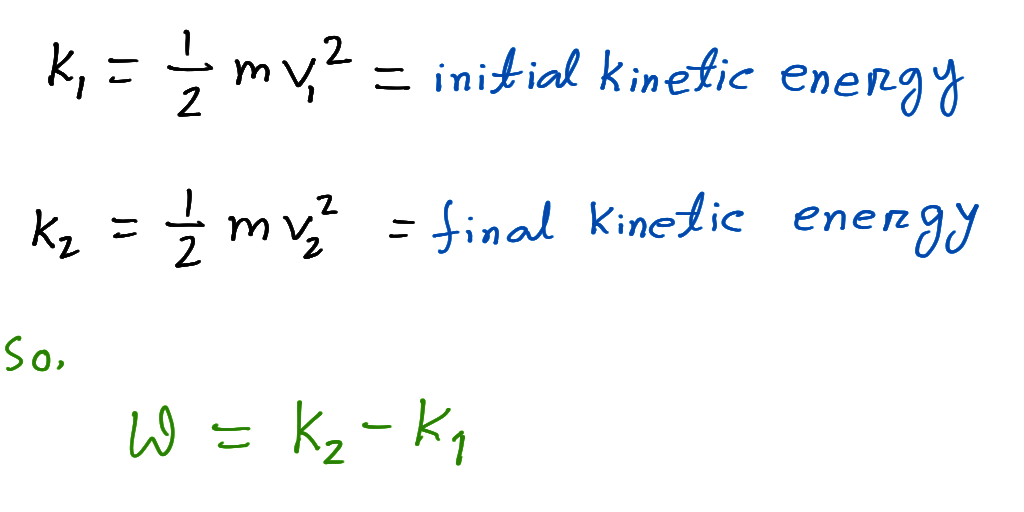
Work Energy Theorem Classical Mechanics By Farhan Tanvir Tushar Open Physics Class Medium
The result based on Newtons laws that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy kinetic energy.

. Question about work energy and the work energy theorem. In Grade 10 you saw that mechanical energy was conserved in the absence of non-conservative forces. Related Threads on Question about.
Therefore we first need to determine the cars kinetic energy at the moment of braking using. The measurement of work and energy with the same unit reinforces the idea that work and energy are related and can be converted into one another. Work is said to be done whenever the force is applied to an object then the object is moved to a certain distance.
You will determine the work done on a nearly frictionless cart and show that the work done is equal to the increase in kinetic energy of the cart. If K represents the change in kinetic energy of the body and W represents the work done on it. The net work on a system equals the change in the quantity.
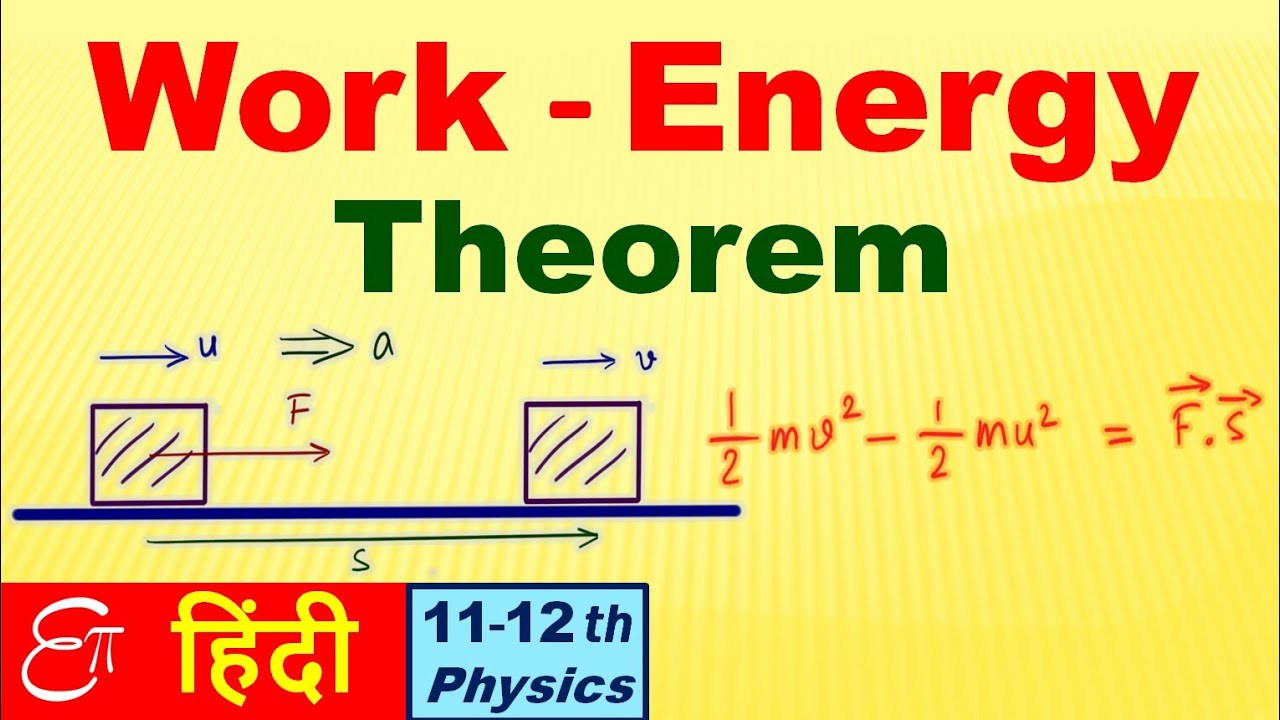
The principle of work and kinetic energy also known as the work-energy theorem states that the work done by the sum of all forces acting on a particle equals the change in. W 1 2 m v f 2 1 2 m v i 2. F is the final kinetic energy and K.
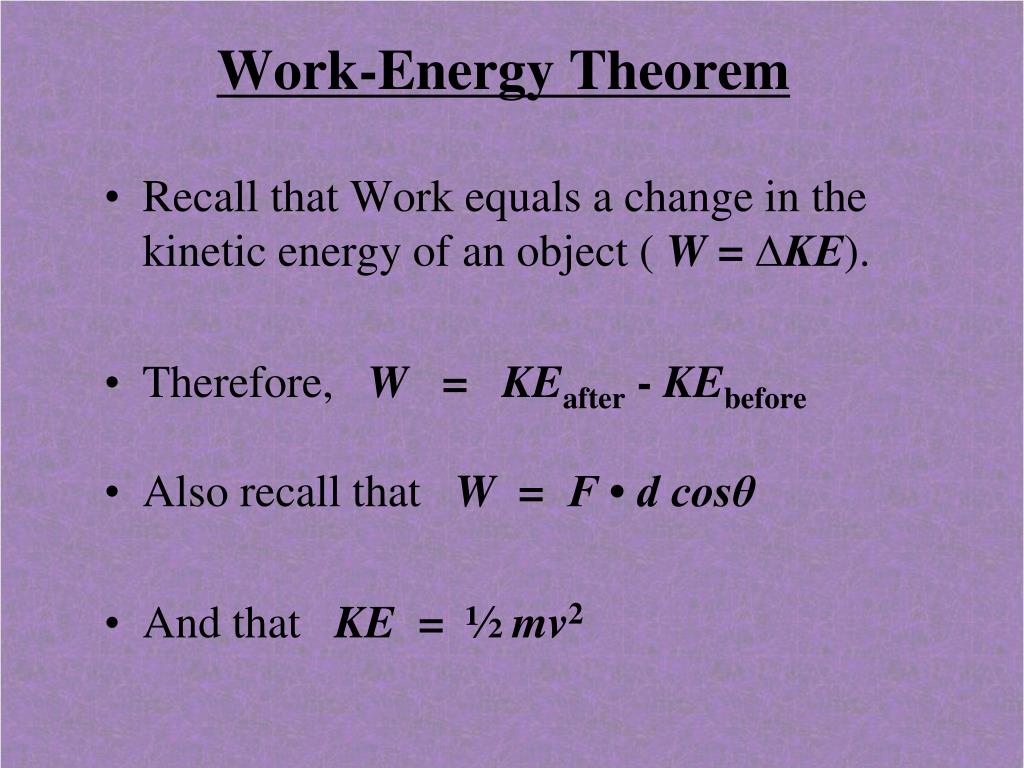
Answer and Explanation. The work-energy theorem asserts that the total amount of work done by forces on an item equals the change in its kinetic energy. The work-energy theorem states that the change in the kinetic energy is equal to the amount of work done.
M is the mass of the object measured using kilograms. Work is said to be done when an acting force displaces a particle. It is a known fact that we all require Energy in order to Work.
Where W is the work done by object measured using Joules. 10 N 10 kgms 2 so 10 J 10 kgm 2 s 2. The principle of work and kinetic energy also known as the work-energy theorem states that the work done by the sum of all forces acting on a particle equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle.
53 Work-energy theorem ESCMD Conservative and non-conservative forces ESCMF. Examples are energy. This relationship is called the workenergy theorem.
The environment has acted on the object and it increases the energy of the object. In this lab we will test the work energy theorem using. Where K f Final kinetic energy.
The work-energy theorem states that the net total work done on a system is equal to its increase in kinetic energy. The quantity 1 2mv2 in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass m moving at a speed v. The work-energy theorem also known as the principle of work and kinetic energy states that the total work done by the sum of all the forces acting on a particle is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of that particle.
Potential energy also referred to as stored energy is the ability of a system to do work due to its position or internal structure. K f K i W. The quantity in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass moving at a speed Translational kinetic energy is distinct from rotational kinetic energy which is considered later.
The Work-Energy Theorem presents a way of dealing with kinematic quantities in mechanics without regard for vector direction. This establishes a relation between work and kinetic energy which is called the Work-Energy Theorem. Work done by an object can be mathematically expressed as.
The total work done on the particle by the force as the particle moves from 1 to 2 is by definition the line integral W12 Z 2 1 F ds 2. Work-Energy Theorem The kinetic energy of a particle of mass m moving with a speed v is defined as T 1 2 mv2. The energy an object has by reason of its motion equal to latexfrac12textmv2latex for the translational ie non-rotational motion of an object of mass m moving at speed v.
So according to the theorem statement we can define the work-energy theorem as follows. If someone could confirm this or explain why this is incorrect it would be very helpful. We apply the work-energy theorem.
The working-energy theorem defines work as the energy change brought on by the velocity change. The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the external forces on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object. It is expressed as.
To validate the work-energy theorem and to study the conservation of energy principle. This explanation can be extended to rigid bodies by describing the work of rotational kinetic energy and torque. When an objects velocity decreases the object has worked on the world and the objects energy decreases.
10 J 10 Nm the units of force multiplied by distance. The work-energy theorem affirms that the work done on any object is comparable to the difference in kinetic energy of the object. You might get tired if you keep standing for a long time.
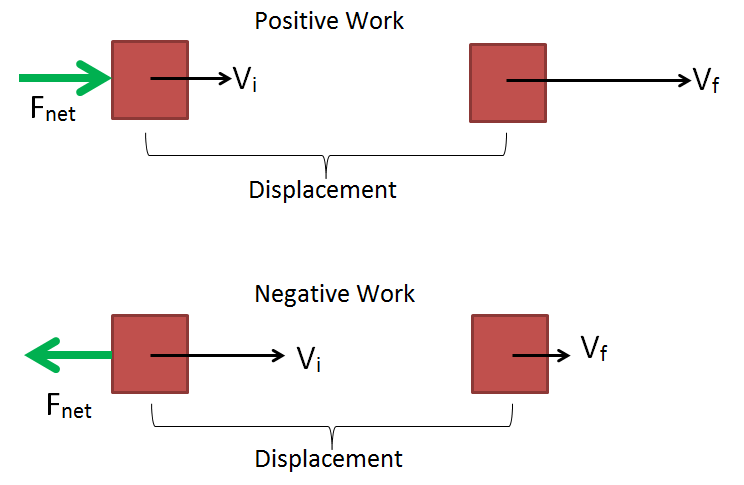
Work and energy are directly proportional to each other. ΔK change in kinetic energy of the object. Work relates to displacement and displacement relates to kinetic energy.
To perform work energy has to be spent. 1 Let us consider a particle that moves from point 1 to point 2 under the action of a force F. When the displacement and the force applied are in an opposite direction.
This definition can be extended to rigid bodies by defining the work of the torque and rotational kinetic energy. O is the original kinetic energy. These directionless quantities such as kinetic energy are called scalars.
Therefore the change in the cars kinetic energy is equal to the work done by the frictional force of the cars brakes. Where W work done in joules J and. If there is no displacement there is no work done.
The joule J is the metric unit of measurement for both work and energy. W net K. Energy is ability to do work.
It is important to know whether a force is an conservative force or an non-conservative force in the system because this is related to whether the force can change an objects total mechanical. We know that all the cars kinetic energy is lost to friction. This relationship is called the workenergy theorem.
The Work-energy theorem explains the reasons behind this Physics of no work. Work and energy are directly proportional to each other.

Work Energy Theorem Variable Force Youtube

Kinetic Energy And The Work Energy Theorem Physics

A State And Prove Work Energy Theorem In The Case Of Const Scholr

Work Energy Theorem Geeksforgeeks
Work Energy Theorem Work Energy Power 2 In Hindi Youtube

Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Work And The Work Energy Principle Video Khan Academy
Work Energy Theorem Energy Education
Ppt Work Energy Theorem Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5571805

State And Explain Work Energy Principle Em4 23 Engineering Mechanics In Tamil Youtube

Work Energy Theorem Classical Mechanics By Farhan Tanvir Tushar Open Physics Class Medium

Kinetic Energy And The Work Energy Theorem Physics

The Work Energy Theorem Objectives Investigate Quantities Using The Work Energy Theorem In Various Situations Calculate Quantities Using The Work Energy Ppt Download
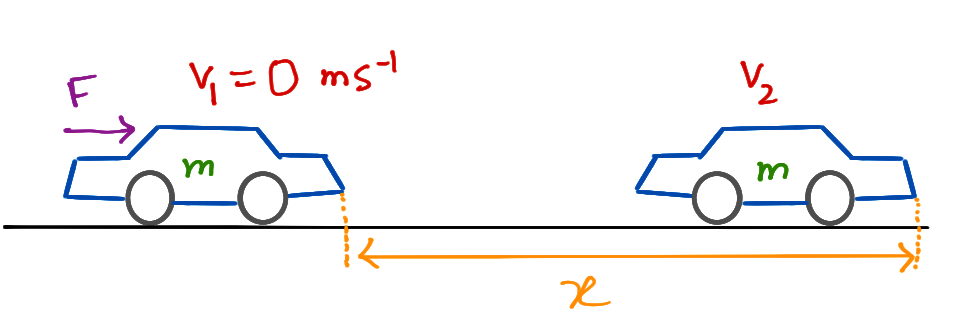
Work Energy Theorem Classical Mechanics By Farhan Tanvir Tushar Open Physics Class Medium

Work Energy Theorem Review Article Khan Academy

Work Energy Theorem Physics Video By Brightstorm
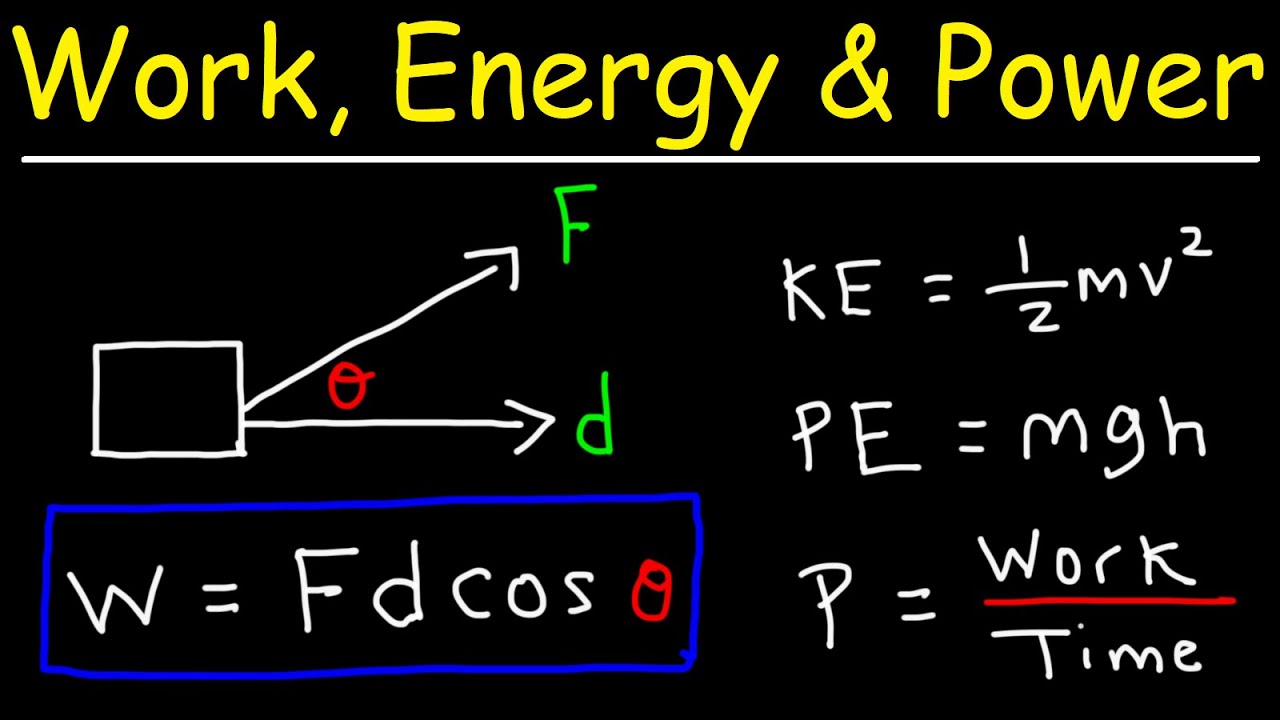
Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Energy Work Power 16 Of 31 Work Energy Principle An Explanation Youtube
